While every company maintains a record of its account balances in its general ledger, financial statements can only be complete and accurate if all accounts are prepared accurately. Unadjusted and Adjusted Trial Balance is done to prepare final accounts which can then be used as a basis for recording adjusting entries to prepare the adjusted trial balance. Preparing an unadjusted trial balance is the fourth step in the accounting cycle. A trial balance is a list of all accounts in the general ledger that have nonzero balances.
When do accountants usually prepare an unadjusted trial balance?
After that, Adjusting Entries will be passed in the relevant accounts to prepare Adjusted Trial Balance, which is the last step before Financial Statements are produced. The articles and research support materials available on this site are educational and are not intended to be investment or tax advice. All such information is provided solely for convenience purposes only and all users thereof should be guided accordingly. The Unadjusted Trial Balance (UTB) document summarizes all of the accounts in an organization at a single point or period.
When to use trial balances
This is vital for understanding the liquidity and financial flexibility of the business. Accurate cash flow information helps management plan for future cash needs and allows investors to gauge the company’s ability to generate cash from its core operations. Accountants call this process ‘balancing the accounts.’ It shows if total debits equal total credits as they should. Making sure these numbers are right is super important for the financial statement to be correct.
- As with the accounting equation, these debit and credit totals must always be equal.
- It lists all the ledger accounts in a summary form which will later be used in the financial statements.
- In other words, a trial balance will show all of the balances of accounts after all transactions have been allowed for, including those which have not yet been entered into a general ledger or subsidiary ledgers.
- It serves to be the source of all financial statements that a company creates.
- Not all accounts in the chart of accounts are included on the TB, however.
- Both the debit and credit columns are calculated at the bottom of a trial balance.
Testing the equality of debits and credits

After the accounts are analyzed, the trial balance can be posted to the accounting worksheet and adjusting journal entries can be prepared. As with all financial reports, trial balances are always prepared with a heading. Typically, the heading consists of three lines containing the company name, name of the trial balance, and date of the reporting period. However, most businesses can streamline this cycle and skip tedious steps like posting transactions to the general ledger and creating a trial balance. Using accounting software like QuickBooks Online can do all these tasks for you behind the scenes. A trial balance is an internal report that itemizes the closing balance of each of your accounting accounts.
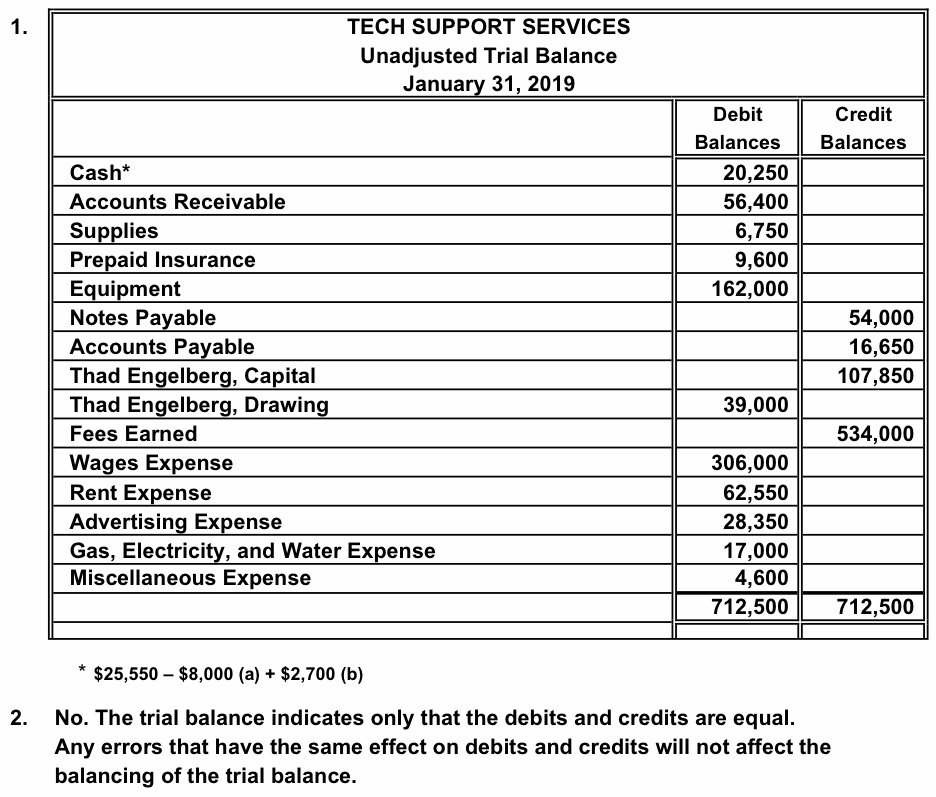
An unadjusted trial balance is a list of all the balances from a company’s accounting ledger before any adjusting entries are made. Creating accurate financial reports starts with a good unadjusted trial balance. Without this foundation, all accounting records could be wrong, leading people who read the reports to make bad choices. Each side—debits and credits—should mirror each other in total if everything is recorded correctly.
The following unadjusted trial balance has been prepared from the ledger accounts of Company A. For example, adjustment to correct over accrual of electricity expenses. Or correcting adjustments when the accountant noted that the debit balance and credit balance of the trial balance are not reconciled due to the incorrect entries made into the general ledgers.
This balance is transferred to the Cash account in the debit column on the unadjusted trial balance. Accounts Payable ($500), Unearned Revenue ($4,000), Common Stock ($20,000) and Service Revenue ($9,500) all have credit final balances in their T-accounts. These credit balances would transfer to the credit column on the unadjusted trial balance. These are costs that a business has incurred but not yet paid or recorded. An example would be utility bills that are due at the end of the month but not paid until the following month.
The debit and credit columns both total $34,000, which means they are equal and in balance. However, just because the column totals are equal and in balance, we are still not guaranteed that a mistake is not present. These adjusting entries have the effect of making certain that the total debits equal the total credits in each account. Business owners and accounting teams rely on the trial balance to create reliable financial statements. A trial balance ensures the accuracy of your accounting system and is just one of the many steps in the accounting cycle. A balanced trial balance hints at no apparent accounting error, whereas discrepancies imply an error somewhere in the account balances.
If they don’t match, accountants know they have some detective work to do to find errors or omissions that could affect financial position accuracy later on. An turbotax rejecting oregon return provides a snapshot of all transactions before any adjustments are made, acting as a checkpoint for accuracy. It’s where we start to ensure every debit matches its corresponding credit and no entry slips through unnoticed. The errors have been identified and corrected, but the closing entries still need to be made before this TB can used to create the financial statements.
